In the world of modern comfort and climate control, HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) systems play a pivotal role. These systems are not only responsible for maintaining pleasant indoor temperatures but also for ensuring good air quality. Among the numerous components that make up an HVAC system, the inductor and liquid level sensor stand out as crucial elements, each contributing to the system's optimal performance in unique ways.
HVAC systems are complex mechanisms designed to heat, cool, and ventilate indoor spaces. They are used in a wide range of settings, from residential homes to large commercial buildings. The heating function is often achieved through furnaces that burn fuel or use electric heating elements. Cooling is typically accomplished by air conditioners or refrigeration systems. Ventilation ensures a continuous supply of fresh air and the removal of stale air.
In HVAC systems, inductors are commonly used in motor control applications. For example, in the motors that drive the fans in an air handling unit (AHU), inductors can monitor the current flow. If there is an abnormal change in the current, it could indicate a problem such as a motor malfunction, a blocked fan blade, or an issue with the electrical supply. By detecting these changes early on, the inductor can trigger an alarm or shut down the system to prevent further damage.
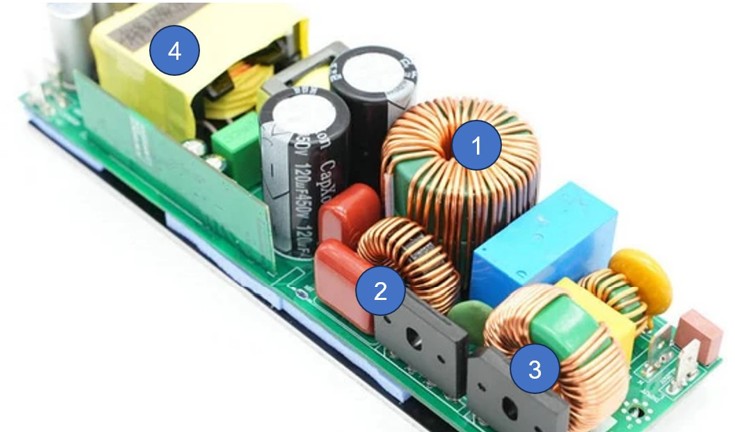
Inductors are also used in power supply, usually if the motor in the HVAC system needs to turn on, there is a rush current when the motor starts, hence inductors are crucial to prevent the system from burning. Take BST's current project with an USA customer for example, there are 4 inductors in a PCBA.

The liquid level sensor is another vital component in HVAC systems. As the name implies, its main function is to monitor the level of liquids within the system. In HVAC systems, there are several areas where liquid level monitoring is crucial. For instance, in the condensate drain pans of air conditioners. When the air is cooled by the air conditioner, moisture condenses and collects in the drain pan. If the liquid level in the drain pan rises too high due to a clogged drain line or excessive condensation, it can lead to water leakage, which can cause damage to the building structure and electrical components. The liquid level sensor continuously monitors the water level in the drain pan. When the level approaches a critical point, it can send a signal to the system's control unit, which may then activate an alarm or initiate a self - cleaning cycle to clear the drain line.
In addition, liquid level sensors are used in the refrigerant storage tanks of HVAC systems. Maintaining the correct refrigerant level is essential for the system's proper functioning. If the refrigerant level is too low, the cooling capacity of the system will be reduced. On the other hand, if the level is too high, it can put excessive pressure on the system components, leading to potential failures. The liquid level sensor ensures that the refrigerant level is constantly monitored, allowing for accurate refrigerant charging and system operation.
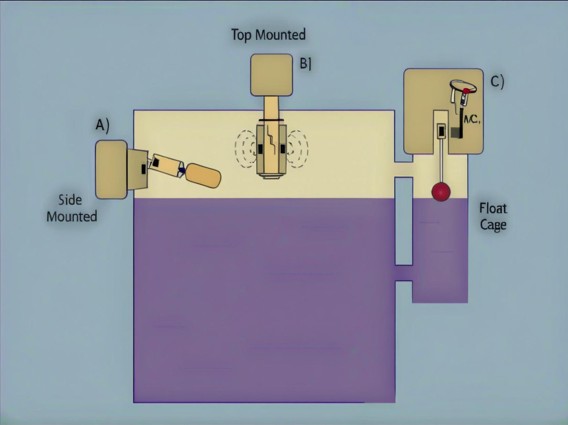
In conclusion, both the inductor and the liquid level sensor are integral parts of an HVAC system. The inductor's ability to detect electrical and environmental changes helps in safeguarding the system's components and ensuring its smooth operation. Meanwhile, the liquid level sensor plays a crucial role in maintaining the proper liquid levels within the system, preventing potential damage caused by water leakage or incorrect refrigerant levels. Understanding the functions of these sensors can help HVAC technicians, building managers, and even homeowners better appreciate the complexity and sophistication of HVAC systems. By ensuring that these sensors are in good working condition, we can optimize the performance of HVAC systems, save energy, and ultimately, create more comfortable and healthy indoor environments.